TPM mechanism required in Windows 11 (Intel PTT, AMD fTPM)
The TPM became famous in Windows 11, but I wasn't very familiar with it. We will discuss what role the TPM has and how it is embedded in the PC. Let's dig into Intel PTT and AMD fTPM from an engineer's point of view.
What is TPM?
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is an independent chip that has a security calculation function and a key storage function.
There are encryption and digital signature mechanisms as security measures, but the fundamental issue is where to put the key.
If you put the key in the HDD, you cannot keep the secret. It will be identified someday just because it is difficult to find.

The point of TPM is that it is outside the HDD and in a place where the CPU cannot be seen directly, and not only the key is stored, but also the functions such as key generation and key verification are confined.
If the key can be taken out, a virus or a hacker who has invaded the PC may take it out, which is meaningless, so it is important that it also has a function to use the key.

Let's compare it to a house.
The TPM is the caretaker of the house.
If there is no caretaker (TPM)
You have the key yourself. You might drop the key somewhere.
In the worst case, the key is hidden under a stone in the garden. It's unlikely to be found, but it's dangerous. The thief may be watching from a distance.
If you have a caretaker (TPM)
The key is kept by the caretaker and cannot be freely entered or exited. You can't even borrow a key. When going in and out, ask the caretaker to open it.
It's like a luxury mansion with security.
TPM physical chip
Before Ivy Bridge of the 3rd generation Core, it was a mechanism to mount a TPM dedicated chip on the motherboard.
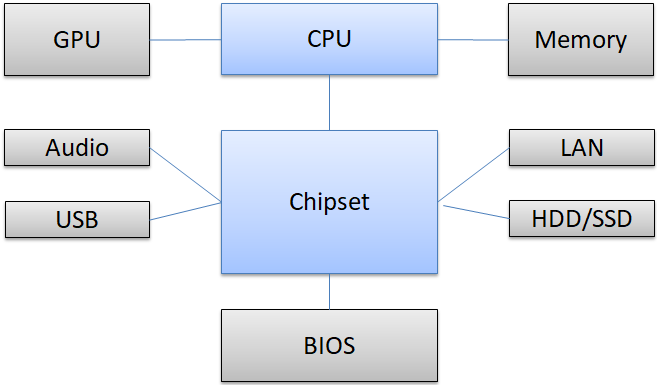
As a mock, modern PCs have devices other than memory and GPU connected to the chipset. The TPM is also connected to the chipset as one of the devices.
Windows runs on the CPU and asks the TPM chip for key generation and authentication.
Some motherboards have empty slots in which the TPM module can be installed.
TPM firmware
Core 4th generation Core Haswell and later no longer require a TPM chip. TPM is a UEFI setting item.
I was wondering if the main CPU would access Flash and the independence realized by the TPM chip could not be achieved.
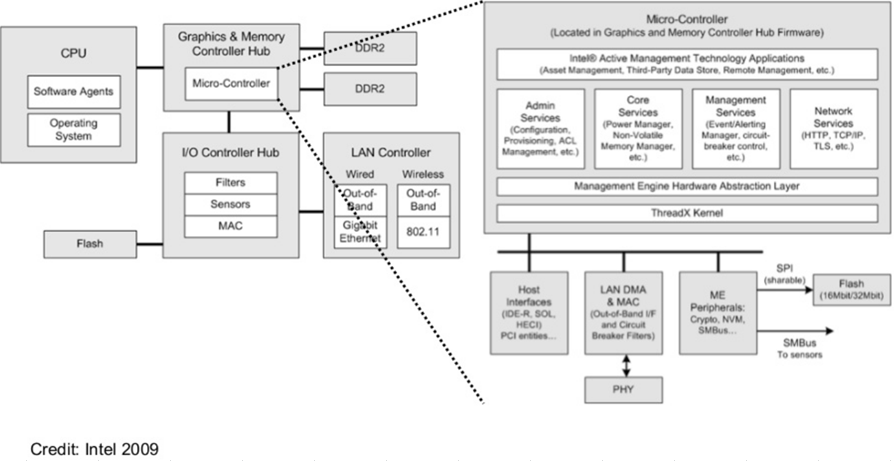
This is where Intel ME, a chipset feature, comes into play. Abbreviation for Intel Management Engine, which controls overall system management. Since Sky Lake, it has been renamed to Intel CSME (Converged Security and Management Engine).
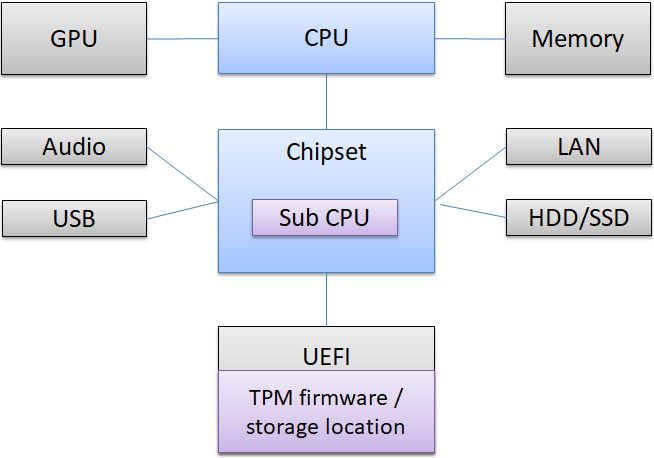
A sub CPU is built into the chipset, and a UNIX-derived OS called MINIX is running. There is another system in the computer that only Intel knows.
Since the device is dominated by the chipset, in fact, the PC with Intel CPU can be interpreted as "Intel chipset is the master and the main CPU is the slave system"
Since the sub CPU has a higher priority than the main CPU, all devices can be freely accessed without the knowledge of the main CPU (that is, Windows or the user). For example, it is possible to intercept or even filter LAN transmission / reception data before passing it to the main CPU. It was pointed out that it is very dangerous in terms of security, but Intel has stated that it is not using it maliciously. It's actually a scary thing that is quite risky.
The main functions of Intel ME are temperature control, fan control, power management, boot guard, etc. The function of the TPM chip has been incorporated as one of these functions.
Sub CPU programs are stored in UEFI FLASH. All functions such as TPM key verification and key information are also saved in Flash memory.
This function is read as "Intel PTT (Platform Trust Technology)". This is in the UEFI settings.
For reference, it is the material at the time of 2009.
AMD has an AMD Platform security processer (PSP) instead of Intel ME. The PSP is built into the CPU, not the chipset. In addition to the x64 core, there is one ARM core for PSP.
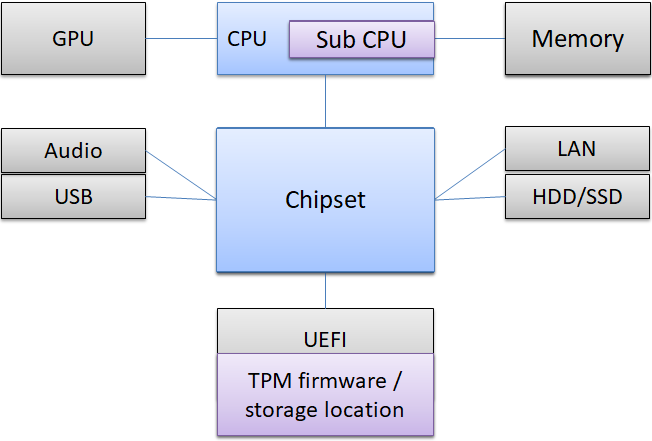
AMD reads this feature as "fTPM". f means firmware.
In this way, an external physical chip is no longer required, and TPM can be realized as chipset firmware. Independence is also maintained by the privilege of the sub CPU of extraterritoriality.
Therefore, when using his TPM on a recent PC, it can be enabled / disabled in the UEFI setting items.
Both Intel and AMD have built their own security environment to support the core. However, these areas have been targeted by hackers and problems have been found. Will the cat-and-mouse game continue at any time?
Intel CSME bug is worse than previously thought | ZDNet